Resonance In Chemistry
Examples showing how different types of bond configurations can be represented using resonance structures. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains.kastatic.org and.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
Theory of resonance, in, theory by which the actual normal state of a molecule is represented not by a single valence-bond structure but by a combination of several distinct structures. The molecule is then said to among the several valence-bond structures or to have a structure that is a of these structures. The energy calculated for a hybrid is lower than the energies of any of the alternative structures; the molecule is then said to be stabilized by resonance. The difference between the energies of any one of the alternative structures and the energy of the resonance hybrid is designated resonance energy.The classic example of the application of the theory of resonance is the formulation of the structure of. The structure of benzene as a six-membered ring of carbon atoms was introduced by the German chemist F.A. Kekule in 1865. Get exclusive access to content from our 1768 First Edition with your subscription.The concept of resonance has similarly been used to formulate structures for polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, molecules containing conjugated systems of double bonds ( e.g., biphenyl, butadiene), free radicals, and other molecules to which no satisfactory single structure in terms of single bonds, double bonds, and triple bonds can be assigned ( e.g., oxygen).
Some general rules are used in the selection of suitable resonance structures for a molecule. These rules are: the structures must have energies of similar magnitudes; the arrangement of the atoms must be approximately the same in all the structures; and the structures must have the same numbers of unpaired electrons.The theory of resonance is based on the fundamental principle of, which states that the representing a of a system can be expressed as a weighted sum of the wave functions that correspond to several structures for the system and that the proper combination is that sum which leads to a minimum calculated energy for the system.
Resonance Structures Table of ContentWhat are Resonance Structures?Resonance structures are sets of Lewis structures that describe the delocalization of electrons in a polyatomic ion or a molecule.In many cases, a single Lewis structure fails to explain the bonding in a molecule/polyatomic ion due to the presence of partial charges and fractional bonds in it. In such cases, resonance structures are used to describe chemical bonding.Resonance in chemistry could be a manner of describing the bonding in particular molecules or ions by merging many contributory structures or forms, jointly called canonical structures or resonance structures within the theory of valence bonding into a hybrid resonance (or hybrid structure). Resonance in ChemistryThe different resonance structures of the carbonate ion (CO 3 2-) are illustrated above. The delocalization of electrons is described via fractional bonds (which are denoted by dotted lines) and fractional charges in a resonance hybrid.Resonance Structures of NO 2 – IonIn the nitrite ion, the bond lengths of both nitrogen-oxygen bonds are equal. The of NO 2 – highlight a difference in the bond order of the two N-O bonds.
Get the embed code Unleash the Archers - Demons of the AstroWaste Album Lyrics1.Astral Annihilation2.Battle In the Shadow (Of the Mountain)3.City of Iron4.Daughters of Winterstone5.Dawn of Ages6.Despair7.General of the Dark Army8.Ripping Through Time9.The Fall of the Galactic Guard10.The Outlander11.The Realm of TomorrowUnleash the Archers Lyrics provided by SongLyrics.comNote: When you embed the widget in your site, it will match your site's styles (CSS). Unleash the archers.
The resonance hybrid of this polyatomic ion, obtained from its different resonance structures, can be used to explain the equal bond lengths, as illustrated below. Resonance Structures of NO2- IonThe resonance hybrid of NO 2 – suggests that each oxygen atom holds a partial charge of magnitude -½.
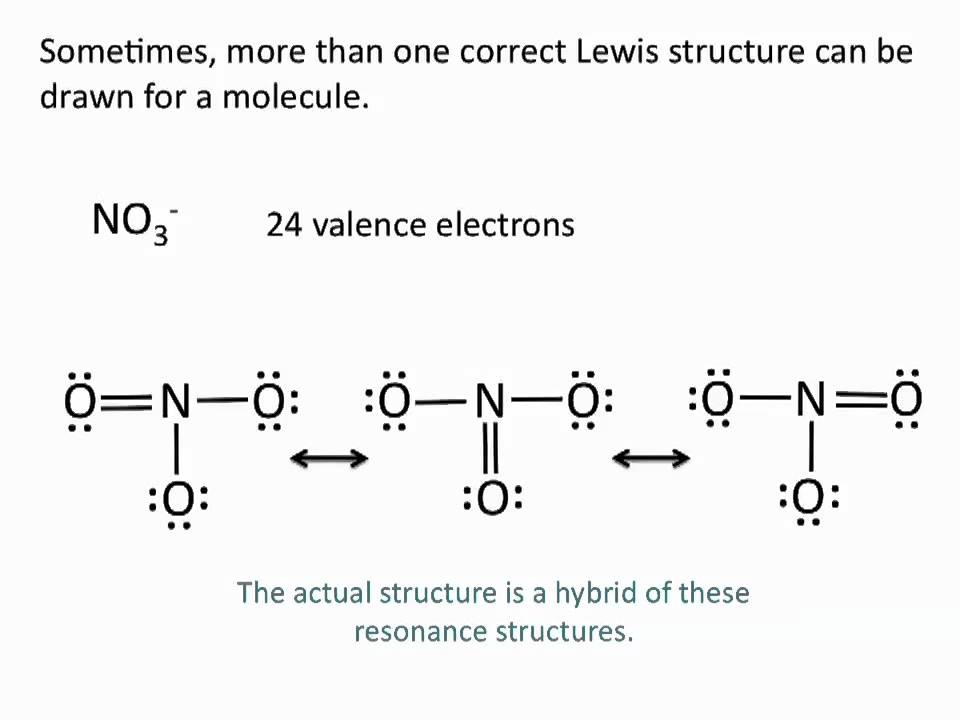
The bond length of the N-O bonds is found to be 125 pm.Resonance Structures of NO 3 – IonNitrogen is the central atom in a nitrate ion. It is singly bonded to two oxygen atoms and doubly bonded to one oxygen atom. The oxygen atoms that are singly bonded to the nitrogen hold a charge of -1 (in order to satisfy the ). The central nitrogen atom has a charge of +1 and the overall charge on the nitrate ion is -1. The three possible resonance structures of NO 3 – are illustrated below. Resonance Structures of NO3- IonIf a resonance hybrid of this polyatomic ion is drawn from the set of Lewis structures provided above, the partial charge on each oxygen atom will be equal to -(⅔). The net charge on the central atom remains +1.
This resonance hybrid is illustrated below.Resonance Structures of O 3The consists of a central oxygen atom which is singly bonded to one oxygen atom and doubly bonded to another. There is no net charge on this molecule, but the Lewis structures of this molecule show a +1 charge on the central oxygen and a -1 charge on the singly bonded oxygen. The two resonance structures of the ozone molecule are illustrated below. Resonance Structures of O3The resonance hybrid of ozone has a +1 charge associated with the oxygen at the centre and a partial charge of -(½) associated with the other oxygen atoms. Resonance Structures of BenzeneBenzene is a very important in organic chemistry. It has the chemical formula C 6H 6. The molecules of benzene have a cyclic structure consisting of alternating single and double bonds between adjacent carbon atoms.
Each carbon atom is also bonded to one hydrogen atom. The two possible resonance structures of benzene are illustrated below. Resonance Structures of BenzeneThe benzene molecule is stabilized by resonance, the pi electrons are delocalized around the ring structure. This delocalization causes each carbon-carbon bond to have a bond order of 1.5, implying that they are stronger than regular C-C sigma bonds.